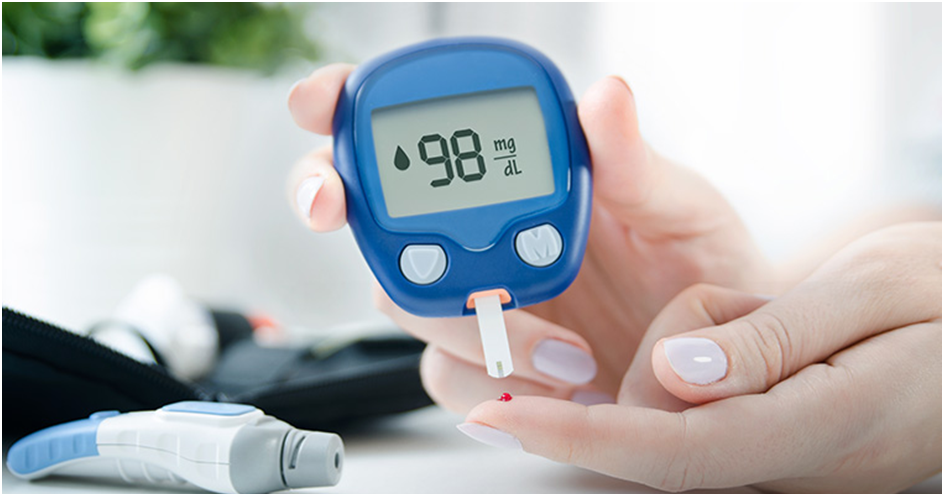
For individuals managing diabetes or those keen on monitoring their blood sugar levels, a blood glucose meter is an indispensable device. This compact and user-friendly tool empowers individuals to measure their blood glucose levels conveniently and regularly, facilitating effective diabetes management. In this article, we’ll explore the features of a blood glucose meter, its benefits, and the importance of regular monitoring for those with diabetes.
Features of a Blood Glucose Meter:
1. Compact Design:
Blood glucose meters are compact and portable, allowing users to carry them easily for on-the-go testing. The small size makes them convenient for use at home, work, or while traveling.
2. Blood Sample Size:
Most meters require only a small blood sample for testing. The use of lancets, which produce a tiny drop of blood, minimizes discomfort and makes the testing process less invasive.
3. Rapid Results:
Blood glucose meters provide rapid results, often within seconds to a minute. This quick turnaround time allows individuals to make timely decisions about their diet, medication, or lifestyle choices.
4. Memory Storage:
Many blood glucose meters come equipped with memory storage capabilities, allowing users to track and review their historical glucose readings. This feature aids in recognizing patterns and trends over time.
5. Easy-to-Read Display:
The display interface of blood glucose meters is designed to be user-friendly, featuring easy-to-read numerical values and often color-coded indicators for quick interpretation of results.
6. Data Connectivity:
Some modern blood glucose meters can connect to smartphones or other devices, enabling users to sync and analyze their glucose data through dedicated apps. This connectivity enhances data management and accessibility.
7. Alternate Site Testing:
Many blood glucose meters allow for alternate site testing, enabling individuals to obtain blood samples from areas like the forearm or palm. This provides flexibility and may be less painful for some users.
Benefits of a Blood Glucose Meter:
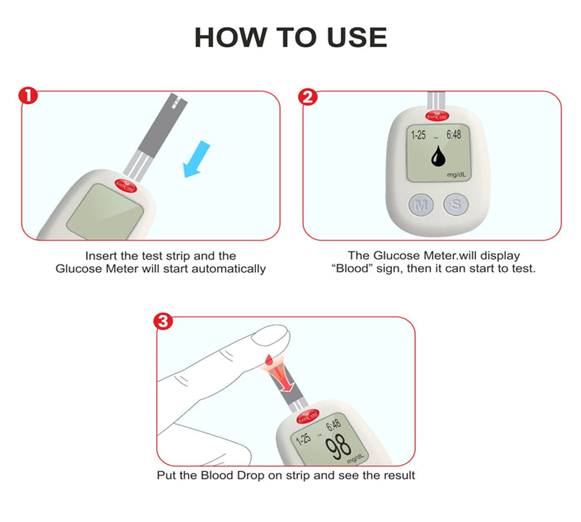
1. Immediate Feedback:
A blood glucose meter provides immediate feedback on blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes management in real time.
2. Personalized Treatment Adjustments:
Regular monitoring with a blood glucose meter enables individuals and healthcare providers to make personalized adjustments to medication, diet, or lifestyle choices based on individual glucose patterns.
3. Prevention of Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia:
By regularly monitoring glucose levels, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent both low (hypoglycemia) and high (hyperglycemia) blood sugar episodes. This contributes to overall diabetes control and reduces the risk of complications.
4. Medication Management:
Blood glucose meters assist individuals in managing their diabetes medications effectively. They provide insights into how the body responds to specific medications, aiding in dosage adjustments when necessary.
5. Understanding Food and Activity Impact:
Monitoring blood glucose levels before and after meals or physical activity helps individuals understand how these factors impact their glucose levels. This knowledge allows for better meal planning and exercise routines.
6. Empowerment in Self-Management:
Regular use of a blood glucose meter empowers individuals with diabetes to take an active role in their self-management. It promotes a sense of control and responsibility for one’s health.
7. Early Detection of Trends:
Tracking glucose readings over time helps identify trends and patterns, such as variations in levels throughout the day or in response to specific triggers. Early detection allows for timely intervention.
Importance of Regular Monitoring for Diabetes Management:
1. Individualized Treatment Plans:
Regular monitoring with a blood glucose meter enables healthcare providers to create individualized treatment plans tailored to a person’s specific needs and response to medications.
2. Prevention of Complications:
Consistent monitoring helps prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular issues, kidney problems, and nerve damage. Maintaining optimal glucose levels contributes to overall health.
3. Optimizing Lifestyle Choices:
By understanding how diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors impact blood glucose levels, individuals can make informed choices to optimize their health and well-being.
4. Early Intervention for Hypoglycemia:
Regular monitoring allows for early detection of low blood sugar levels, enabling individuals to take prompt action to prevent severe hypoglycemic events.
5. Treatment Adjustments as Needed:
Blood glucose meter readings guide timely adjustments to medication dosages, ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate amount of insulin or other diabetes medications.
6. Enhanced Quality of Life:
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels contributes to an improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes. It reduces the likelihood of diabetes-related complications and supports overall well-being.
7. Patient Empowerment:
Regular monitoring empowers individuals to actively manage their diabetes, fostering a sense of control and confidence in their ability to make informed decisions about their health.
Safety Considerations:
1. Proper Hygiene:
Ensure proper hygiene when using a blood glucose meter. Wash hands thoroughly before testing, and follow the recommended cleaning and maintenance guidelines for the meter and testing supplies.
2. Regular Calibration:
Calibrate the blood glucose meter regularly, as recommended by the manufacturer. Regular calibration helps maintain the accuracy of the readings.
3. Storage of Testing Supplies:
Store testing supplies, including test strips and lancets, in a cool and dry place. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper storage to ensure the integrity of the supplies.
4. Battery Checks:
Check the battery status of the blood glucose meter regularly. A low battery can affect the accuracy of the readings, so it’s essential to replace the battery as needed.
5. Consultation with Healthcare Providers:
Collaborate with healthcare providers to establish a testing schedule and determine target glucose ranges. Regularly discuss glucose readings and any concerns with healthcare professionals to receive guidance and adjustments to the diabetes management plan.
Conclusion:
A blood glucose meter serves as a valuable tool in the proactive management of diabetes, providing individuals with real-time insights into their blood sugar levels. With its compact design, rapid results, and data connectivity features, the blood glucose meter enhances the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies. By fostering regular monitoring, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health, make informed decisions, and work collaboratively with healthcare providers to achieve optimal glucose control and overall well-being.